 SOLVING QUADRATIC EQUATIONS
SOLVING QUADRATIC EQUATIONS  SOLVING QUADRATIC EQUATIONS
SOLVING QUADRATIC EQUATIONS 
Note:
 Factoring
Factoring
 Completing the Square
Completing the Square
 Quadratic Formula
Quadratic Formula
 Graphing
Graphing
Solve for x in the following equation.
Example 2: 
![]()
The equation is already equal to zero.
Method 1:  Factoring
Factoring
The equation can be written in the equivalent form of ![]() The only way that a product can equal zero is if one
or both of the factors equal zero.
The only way that a product can equal zero is if one
or both of the factors equal zero.

The answers are ![]()
Method 2:  Completing the square
Completing the square
Subtract 5 from both sides of the equation.
![]()
Add 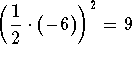 to both sides of the equation.
to both sides of the equation.
![]()
Factor the left side and simplify the right side.
![]()
Take the square root of both sides of the equation,
![]()
Add 3 to both sides of the equation.

![]()
Method 3:  Quadratic Formula
Quadratic Formula
The quadratic formula is 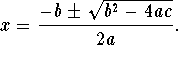
In the equation ![]() , a is the coefficient of the
, a is the coefficient of the ![]() term, b is the coefficient of the x term, and c is the
constant. Simply insert 1 for a, -6 for b, and 5 for
c in the quadratic formula and simplify
term, b is the coefficient of the x term, and c is the
constant. Simply insert 1 for a, -6 for b, and 5 for
c in the quadratic formula and simplify
.
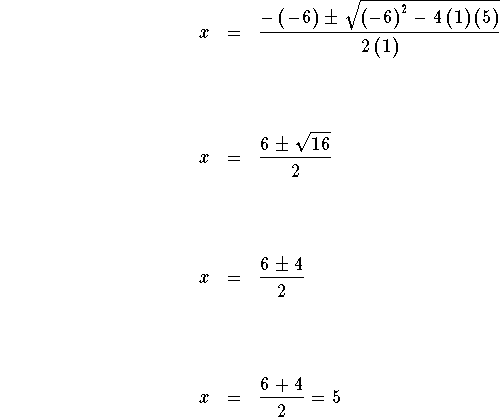
![]()
Method 4:  Graphing
Graphing
Graph y= the left side of the equation or ![]() and graph y=
the right side of the equation or y=0. The graph of y=0 is nothing more
than the x-axis. So what you will be looking for is where the graph of
and graph y=
the right side of the equation or y=0. The graph of y=0 is nothing more
than the x-axis. So what you will be looking for is where the graph of ![]() crosses the x-axis. Another way of saying this is that the
x-intercepts are the solutions to this equation.
The x-intercepts are 1 and
crosses the x-axis. Another way of saying this is that the
x-intercepts are the solutions to this equation.
The x-intercepts are 1 and ![]() The answers are 1 and
The answers are 1 and ![]()
Check these answers in the original equation.
Check the answer x=1 by substituting 1 in the original equation for x. If the left side of the equation equals the right side of the equation after the substitution, you have found the correct answer.
Check the solution x=5 by substituting 5 in the original equation for x. If the left side of the equation equals the right side of the equation after the substitution, you have found the correct answer.
Since the left side of the original equation is equal to the right side of
the original equation after we substitute the value 5 for x, then x=5 is
a solution.
If you would like to test yourself by working some problems similar to this example, click on Problem.
If you would like to go back to the equation table of contents, click on Contents.

