 EQUATIONS INVOLVING
FRACTIONS (RATIONAL EQUATIONS)
EQUATIONS INVOLVING
FRACTIONS (RATIONAL EQUATIONS)
 EQUATIONS INVOLVING
FRACTIONS (RATIONAL EQUATIONS)
EQUATIONS INVOLVING
FRACTIONS (RATIONAL EQUATIONS)

Note:
If you would like an in-depth review of fractions, click on Fractions.
Problem 5.3d:
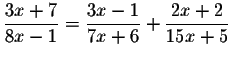
Answer:x=7
Solution:
Recall that you cannot divide by zero. Therefore, the
first fraction is valid if ,
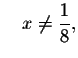 the second
fraction is valid if
the second
fraction is valid if
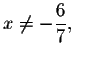 and the third
fraction is valid is
and the third
fraction is valid is
 If
If
![]()
![]() , or
, or
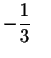 turn out to be the solutions,
you must discard them as extraneous solutions.
turn out to be the solutions,
you must discard them as extraneous solutions.
Multiply both sides by the least common multiple
![]() (the smallest number that all
the denominators will divide into evenly). This step will eliminate all the
denominators.
(the smallest number that all
the denominators will divide into evenly). This step will eliminate all the
denominators.
![\begin{eqnarray*}\displaystyle \frac{3x+7}{8x-1} &=&\displaystyle \frac{3x-1}{7x...
...ystyle \frac{3x-1}{7x+6}+\displaystyle \frac{2x+2}{15x+5}\right]
\end{eqnarray*}](img11.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}\left( 8x-1\right) \left( 7x+6\right) \left( 15x+5\right) \left...
...ft( 15x+5\right) \left[ \displaystyle \frac{
2x+2}{15x+5}\right]
\end{eqnarray*}](img12.gif)
which is equivalent to
![\begin{eqnarray*}\displaystyle \frac{\left( 8x-1\right) \left( 7x+6\right) \left...
...15x+5\right) }{1}
\left[ \displaystyle \frac{2x+2}{15x+5}\right]
\end{eqnarray*}](img13.gif)
which can be rewritten as
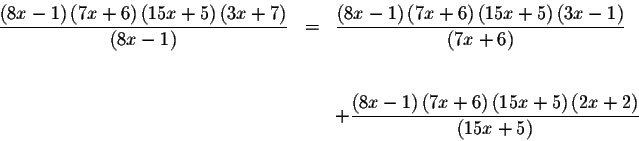
which can be rewritten as
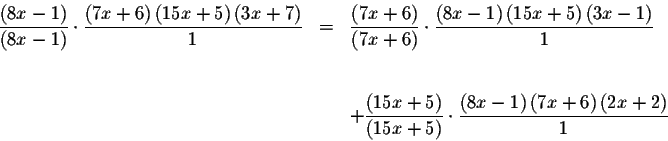
which can be simplified to
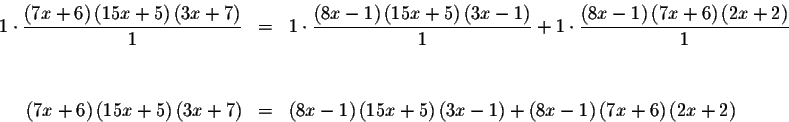
![\begin{eqnarray*}\left( 7x+6\right) \left[ \left( 15x+5\right) \left( 3x+7\right...
...ight] -1\left[ 45x^{2}-5\right] +8x\left[ 14x^{2}+26x+12\right]
\end{eqnarray*}](img17.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&&-1\left[ 14x^{2}+26x+12\right] \\
&& \\
&& \\
315x^{3}+840...
...40x-45x^{2}+5+112x^{3}+208x^{2}+96x \\
&& \\
&&-14x^{2}-26x-12
\end{eqnarray*}](img18.gif)
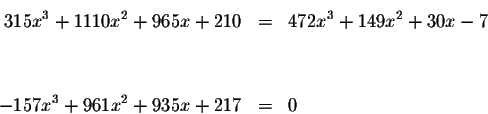
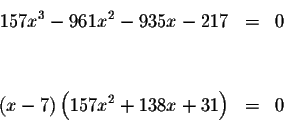
The only way the product of two expressions equals zero if at least one of
the expressions is zero.
To determine what values of x will cause the expression
![]() to equal zero, we use the Quadratic Formula
to equal zero, we use the Quadratic Formula
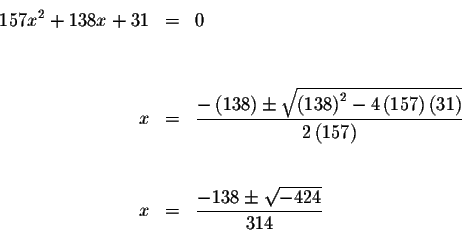
Since you cannot compute the square root of a negative number in the real number system, these two solutions are not real.
The only real solution is
![]()
Check the solution x=7 by substituting 7 in the original equation for x. If the left side of the equation equals the right side of the equation after the substitution, you have found the correct answer.
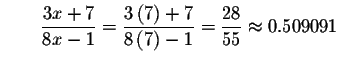
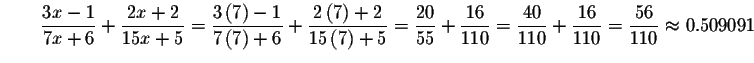
You can also check your answer by graphing
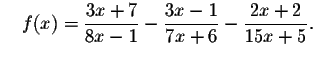 (formed by subtracting the right side of the original equation from the left
side). Look to see where the graph crosses the x-axis; that will be the real
solution. Note that the graph crosses the x-axis at one place: x=7.
(formed by subtracting the right side of the original equation from the left
side). Look to see where the graph crosses the x-axis; that will be the real
solution. Note that the graph crosses the x-axis at one place: x=7.
This verifies our solution graphically.
We have verified our solution both algebraically and graphically.

