 EQUATIONS INVOLVING
FRACTIONS (RATIONAL EQUATIONS)
EQUATIONS INVOLVING
FRACTIONS (RATIONAL EQUATIONS)
 EQUATIONS INVOLVING
FRACTIONS (RATIONAL EQUATIONS)
EQUATIONS INVOLVING
FRACTIONS (RATIONAL EQUATIONS)

Note:
If you would like an in-depth review of fractions, click on Fractions.
Solve for x in the following equation.
If you would like to see the answers and the solutions, click on solution.
Problem 5.4a:
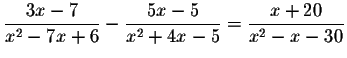
Problem 5.4b:
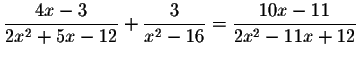
Problem 5.4c:
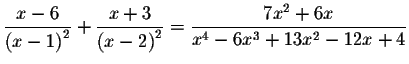
If you would like to go back to the equation table of contents, click on contents.

