 SOLVING TRIGONOMETRIC EQUATIONS
SOLVING TRIGONOMETRIC EQUATIONS SOLVING TRIGONOMETRIC EQUATIONS
SOLVING TRIGONOMETRIC EQUATIONS
Note: If you would like a review of trigonometry, click on trigonometry.
Problem 9.12d: Solve for x in the equation
Answer: The exact answers are
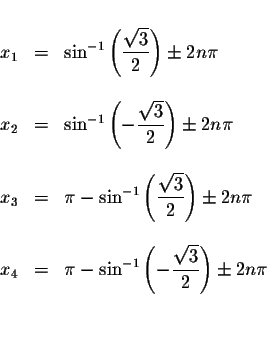
where n is an integer.
The approximate values of these solutions are

Original Equation:
![]()
Solution:
There are an infinite number of solutions to this problem. Let's simplify
the problem by rewriting it in an equivalent factored form.
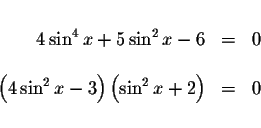
The only way the product equals zero is if at least one of the factors
equals zero. Therefore,
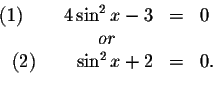
Let's first solve for ![]() in equations
in equations
![]() and
and
![]()
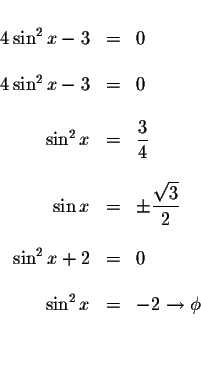
How do we isolate the x in each of these equations? We could take the inverse (arcsine) of both sides of the equations. However, the sine function is not a one-to-one function.
Let's restrict the domain so the function is one-to-one on the restricted
domain while preserving the original range. The sine function is one-to-one
on the interval
![$\left[ -\displaystyle \displaystyle \frac{\pi }{2},\displaystyle \displaystyle \frac{\pi }{2}\right] .$](img12.gif) If we
restrict the domain of the sine function to that interval , we can take the
arcsine of both sides of each equation.
If we
restrict the domain of the sine function to that interval , we can take the
arcsine of both sides of each equation.
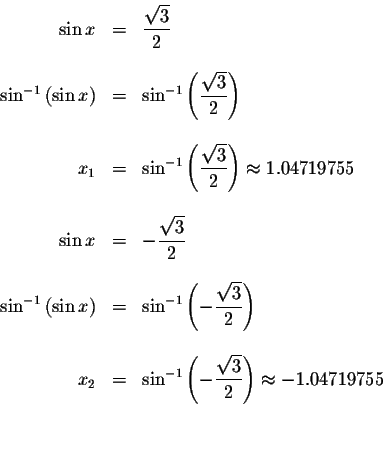
We know that
![]() ,
therefore if
,
therefore if
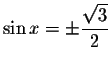 ,
then
,
then
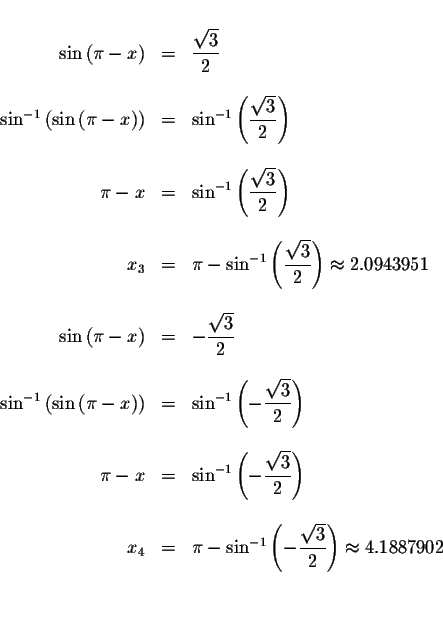
Since the period of ![]() equals
equals ![]() ,
these solutions will repeat
every
,
these solutions will repeat
every ![]() units. The exact solutions are
units. The exact solutions are
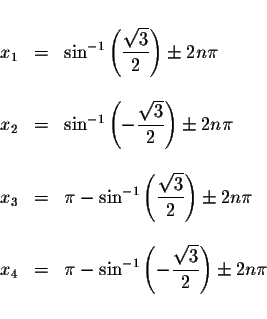
where n is an integer.
The approximate values of these solutions are

where n is an integer.
Original Equation:
![]()
You can check each solution algebraically by substituting each solution in the original equation. If, after the substitution, the left side of the original equation equals the right side of the original equation, the solution is valid.
You can also check the solutions graphically by graphing the function formed by subtracting the right side of the original equation from the left side of the original equation. The solutions of the original equation are the x-intercepts of this graph.
Algebraic Check:
Check solution
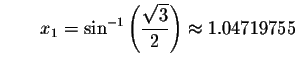
Left Side:
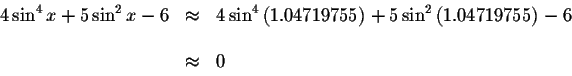
Right Side: ![]()
Since the left side of the original equation equals the right side of the original equation when you substitute 1.04719755 for x, then 1.04719755is a solution.
Check solution
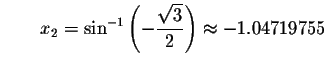
Left Side:
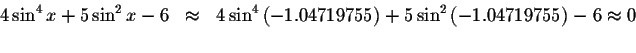
Right Side: ![]()
Since the left side of the original equation equals the right side of the original equation when you substitute -1.04719755 for x, then -1.04719755is a solution.
Check solution
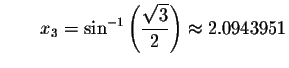
Left Side:
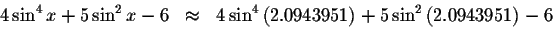
Right Side: ![]()
Since the left side of the original equation equals the right side of the original equation when you substitute 2.0943951 for x, then 2.0943951 is a solution.
Check solution
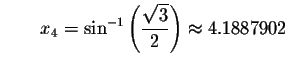
Left Side:
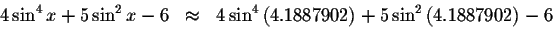
Right Side: ![]()
Since the left side of the original equation equals the right side of the original equation when you substitute 4.1887902 for x, then 4.1887902 is a solution.
Graphical Check:
Graph the function
![]() ,
formed by subtracting
the right side of the original equation from the left side of the original
equation. The x-intercepts are the real solutions.
,
formed by subtracting
the right side of the original equation from the left side of the original
equation. The x-intercepts are the real solutions.
Note that the graph crosses the x-axis many times indicating many solutions. Let's check a few of these x-intercepts against the solutions we derived.
Verify the graph crosses the x-axis at
1.04719755. Since the period is
![]() ,
you can verify that the graph also crosses the
x-axis again at
1.04719755+6.2831853=7.3303829 and at
,
you can verify that the graph also crosses the
x-axis again at
1.04719755+6.2831853=7.3303829 and at
![]() ,
etc.
,
etc.
Verify the graph crosses the x-axis at
-1.04719755. Since the period is
![]() ,
you can verify that the graph also crosses the
x-axis again at
-1.04719755+6.2831853=5.2359878 and at
,
you can verify that the graph also crosses the
x-axis again at
-1.04719755+6.2831853=5.2359878 and at
![]() ,
etc.
,
etc.
Verify the graph crosses the x-axis at
2.0943951. Since the period is
![]() ,
you can verify that the graph also crosses the x-axis
again at
2.0943951+6.2831853=8.37758 and at
,
you can verify that the graph also crosses the x-axis
again at
2.0943951+6.2831853=8.37758 and at
![]() ,
etc.
,
etc.
Verify the graph crosses the x-axis at
4.1887902. Since the period is
![]() ,
you can verify that the graph also crosses the x-axis
again at
4.1887902+6.2831853=10.4719755 and at
,
you can verify that the graph also crosses the x-axis
again at
4.1887902+6.2831853=10.4719755 and at
![]() ,
etc.
,
etc.
Note: If the problem were to find the solutions in the interval
![]() ,
then you choose those solutions from the set of infinite
solutions that belong to the set
,
then you choose those solutions from the set of infinite
solutions that belong to the set
![]()
![]() ,
4.1887902 and
,
4.1887902 and
![]()
If you would like to review the solution of another problem, click on
solution.
If you would like to go back to the equation table of contents, click on Contents.

