
 SOLVING TRIGONOMETRIC EQUATIONS
SOLVING TRIGONOMETRIC EQUATIONS

Note: If you would like a review of trigonometry, click on trigonometry.
Problem 9.7c: Solve for x in the equation
Answer: The exact answers are
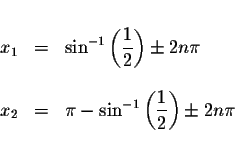
where n is an integer.
The approximate values of these solutions are
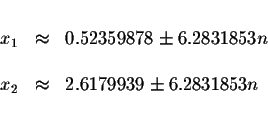
Solution:
There are an infinite number of solutions to this problem.
In the equation
![]() there are two different
trigonometric terms. To simplify the solution, convert the equation to an
equivalent equation with just sine terms of just cosine terms. Which one
shall it be? The easiest way is to convert the trigonometric terms to sine
terms because you can solve for
there are two different
trigonometric terms. To simplify the solution, convert the equation to an
equivalent equation with just sine terms of just cosine terms. Which one
shall it be? The easiest way is to convert the trigonometric terms to sine
terms because you can solve for
![]() in the identity
in the identity
![]()
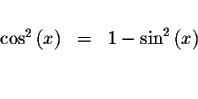


The only way the product of two factors equals zero is if at least one of
the factors equals zeros. This means that
![]() if
if
![]() or
or
![]()
We have transformed a difficult problem into two problems. To find the
solutions to the original equation,
![]() ,
we first solve for
,
we first solve for
![]() in the equations
in the equations
![]() and
and
![]()
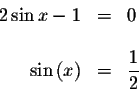
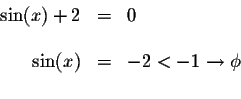
To solve for x, we must isolate the x. How do we do that? We could take the <tex2htmlcommentmark> arcsine of both sides. However, the sine function is not a one-to-one function.
We can restrict the domain of the ![]() function so it is one-to-one on
the restricted domain while preserving the original range. The sinefunction is one-to-one on the interval
function so it is one-to-one on
the restricted domain while preserving the original range. The sinefunction is one-to-one on the interval
![$\left[ -\displaystyle \displaystyle \frac{\pi }{2},\displaystyle \displaystyle \frac{\pi }{%
2}\right] .$](img22.gif) If we restrict the domain of the sine function to that
interval , we can take the arcsine of both sides of each equation.
If we restrict the domain of the sine function to that
interval , we can take the arcsine of both sides of each equation.
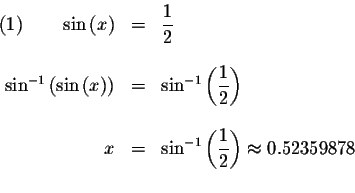
We know that
![]() Therefore,
if
Therefore,
if
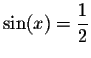 ,
then
,
then
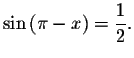
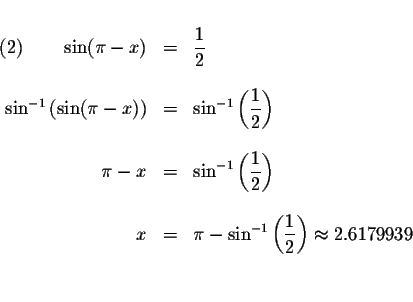
Since the period of ![]() equals
equals ![]() ,
these solutions will repeat
every
,
these solutions will repeat
every ![]() units. The exact solutions are
units. The exact solutions are

where n is an integer.
The approximate values of these solutions are

where n is an integer.
You can check each solution algebraically by substituting each solution in the original equation. If, after the substitution, the left side of the original equation equals the right side of the original equation, the solution is valid.
You can also check the solutions graphically by graphing the function formed by the left side of the original equation and graphing the function formed by the right side of the original equation. The x-coordinates of the points of intersection are the solutions. The right side of the equation is 0 and <tex2htmlcommentmark> f(x)=0 is the x-axis. So really what you are looking for are the x-intercepts to the function formed by the left side of the equation.
Algebraic Check:
Check solution
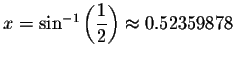
Left Side:
Right Side: ![]()
Since the left side of the original equation equals the right side of the original equation when you substitute 0.52359878 for x, then 0.52359878is a solution.
Check solution
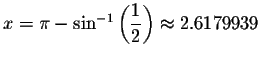
Left Side:
Right Side: ![]()
Since the left side of the original equation equals the right side of the original equation when you substitute 2.6179939 for x, then 2.6179939 is a solution.
The exact solutions are
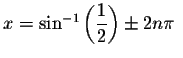 and
and
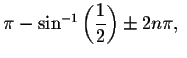 and these
solutions repeat every
and these
solutions repeat every ![]() units. The approximate values of these
solutions are
units. The approximate values of these
solutions are
![]() and 2.6179939 and these solutions
repeat every
and 2.6179939 and these solutions
repeat every
![]() units.
units.
Graphical Check:
Graph the equation
![]() Note that the graph
crosses the x-axis many times indicating many solutions.
Note that the graph
crosses the x-axis many times indicating many solutions.
Verify the graph crosses the x-axis at
0.52359878. Since the period is
![]() ,
the graph also crosses the x-axis again at
<tex2htmlcommentmark>
0.52359878+6.2831853=6.806784 and at
,
the graph also crosses the x-axis again at
<tex2htmlcommentmark>
0.52359878+6.2831853=6.806784 and at
![]() ,
etc.
,
etc.
Verify the graph crosses the x-axis at
![]() .
Since the period is
.
Since the period is
![]() ,
the graph also crosses the x-axis again at
<tex2htmlcommentmark>
2.6179939+6.2831853=8.901179 and at
,
the graph also crosses the x-axis again at
<tex2htmlcommentmark>
2.6179939+6.2831853=8.901179 and at
![]() ,
etc.
,
etc.
Note: If the problem were to find the solutions in the interval
![]() ,
then you choose those solutions from the set of infinite
solutions that belong to the set
,
then you choose those solutions from the set of infinite
solutions that belong to the set
![]()
![]() and
and
![]()
If you would like to review the solution to another problem, click Back to Solutions and then click on the word solution opposite the problem you want to review.
If you would like to go to the next section, click on Next.
If you would like to go back to the previous section, click on previous.
If you would like to go back to the equation table of contents, click on Contents.

