 Taylor Polynomials
Taylor Polynomials
 Taylor Polynomials
Taylor Polynomials
The fundamental idea in differential calculus is that a function can be ``locally'' approximated by its tangent line.
For instance consider the function ![]() near
near ![]() .
Since its derivative at
.
Since its derivative at ![]() equals
equals ![]() , the tangent line at
, the tangent line at ![]() can be written as
can be written as
![]()
In the picture below, the sine function is black, while its tangent line is depicted in red. Close to ![]() , both are quite close!
, both are quite close!
 |
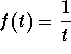 at the point
at the point