 GRAPHS OF LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS
GRAPHS OF LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS

In this section we will illustrate, interpret, and discuss the graphs of logarithmic functions. Recall that whenever there is a minus sign in front of the logarithmic term, it means that there is a reflection across the x-axis. Recall also that whenever there is a minus sign in front of the x in the argument, it means that there is a reflection across the y-axis.
Horizontal and Vertical Shifts and Reflection Across the x-axis: The following examples discuss the difference between the graph of f(x) and the graph of -f(x + A) + B
Example 11: Graph the function 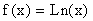 and the function
and the function 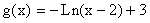 on the same rectangular coordinate system. and answer the following questions about each graph:
on the same rectangular coordinate system. and answer the following questions about each graph:
- In what quadrants in the graph of the function
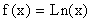 located? In what quadrants is the graph of the function
located? In what quadrants is the graph of the function 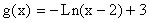 located?
located?
- What is the x-intercept and the y-intercept on the graph of the function
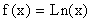 ? What is the x-intercept and the y-intercept on the graph of the function
? What is the x-intercept and the y-intercept on the graph of the function 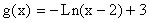 ?
?
- Find the point (2, f(2)) on the graph of
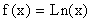 and find (4, g(4)) on the graph of
and find (4, g(4)) on the graph of 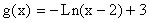 . What do these two points have in common?
. What do these two points have in common?
- Describe the relationship between the two graphs.
- How would you moved the graph of
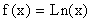 so that it would be superimposed on the graph of
so that it would be superimposed on the graph of 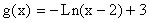 ? When you moved the graph, where would the point (1, 0) on
? When you moved the graph, where would the point (1, 0) on 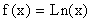 be after the move?
be after the move?
- You can see that the both graphs are located in quadrants I and IV.
- You can see that neither of the graphs crosses the y-axis; therefore, neither of the graphs has a y-intercept. Notice that the graph of f(x) crosses the x-axis at 1 because
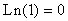 . The graph of g(x) crosses the x-axis at 22.085537 because
. The graph of g(x) crosses the x-axis at 22.085537 because  when x = 22,085537.
when x = 22,085537.
- The point
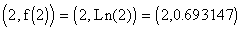 is located on the graph of
is located on the graph of 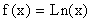 . The point
. The point 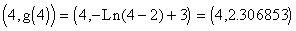 is located on the graph of
is located on the graph of 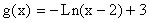 .
.
- Both graphs have the same shape. It appears that the graph of
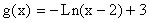 is the result of reflecting the graph
is the result of reflecting the graph 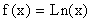 over the x-axis, then shifting the graph to the right and upward.
over the x-axis, then shifting the graph to the right and upward.
- After we reflect the graph across the x-axis, the point (1,0) stays the same. After the graph is then moved to the right 2 units and up 3 units, it would be superimposed on the graph of
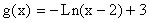 . The point (1, 0) on the graph of
. The point (1, 0) on the graph of 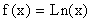 would first be shifted to the right 2 units and up 3 units to (1 + 2, 0 + 3) or (3, 3).
would first be shifted to the right 2 units and up 3 units to (1 + 2, 0 + 3) or (3, 3).
Example 12: Graph the function 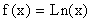 and the function
and the function 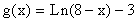 on the same rectangular coordinate system. Answer the following questions about each graph:
on the same rectangular coordinate system. Answer the following questions about each graph:
- In what quadrants in the graph of the function
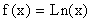 located? In what quadrants is the graph of the function
located? In what quadrants is the graph of the function 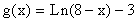 located?
located?
- State the domain of both functions.
- What is the x-intercept and the y-intercept on the graph of the function
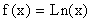 ? What is the x-intercept and the y-intercept on the graph of the function
? What is the x-intercept and the y-intercept on the graph of the function 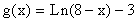 ?
?
- Find the point (2, f(2)) on the graph of
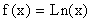 and find (6, g(6)) on the graph of
and find (6, g(6)) on the graph of 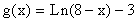
- What do these two points have in common?
- Describe the relationship between the two graphs.
- Describe how you would move the graph of
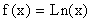 moved so that it would be superimposed on the graph of
moved so that it would be superimposed on the graph of 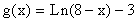 . Where would the point (1, 0) on the graph of
. Where would the point (1, 0) on the graph of 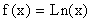 wind up on after the move?
wind up on after the move?
- The graph of
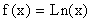 is located in quadrants I and IV. The graph of
is located in quadrants I and IV. The graph of 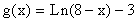 is located in quadrants II, III and IV.
is located in quadrants II, III and IV.
- The domain of
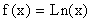 is the set of all positive real numbers. The graph of
is the set of all positive real numbers. The graph of 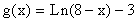 is the set of real numbers less than 8.
is the set of real numbers less than 8.
- The graph of
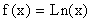 does not cross the y-axis. It crosses the x-axis at 1.
does not cross the y-axis. It crosses the x-axis at 1.
The graph of 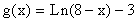 crosses the x-axis at -12.085537 because
crosses the x-axis at -12.085537 because 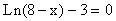 when x = -12.085537. It crosses the y-axis at -0.920558 because
when x = -12.085537. It crosses the y-axis at -0.920558 because  .
.
- The point
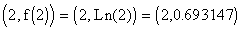 is located on the graph of
is located on the graph of 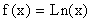 . The point
. The point 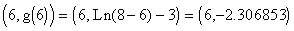 is located on the graph of
is located on the graph of 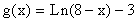 .
.
- The point (6, g(6)) is located to the right and down from the point (2, f(2)).
- Both graphs have the same shape. The graph of
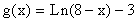 opens to the left whereas the graph of
opens to the left whereas the graph of 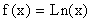 opens to the right. There are horizontal and vertical shifts.
opens to the right. There are horizontal and vertical shifts.
Whenever there is a minus in front of the x, it means there is a reflection across the y-axis. Whenever something is added or subtracted from the x in the argument, it means there is a horizontal shift. Whenever a constant is added to the logarithmic term, it means there is a vertical shift.
- Rewrite the equation
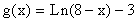 by factoring out -1 from the argument to read
by factoring out -1 from the argument to read 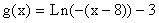 .
.
From the equation, you can see that there is a reflection across the y-axis (minus sign in front of the x), a horizontal shift will be to the right 8 units, and a vertical shift down 3 units.
Therefore, reflect the graph of 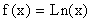 over the y-axis and then shift (move) the reflected graph to the right 8 units and down 3 units. The point (1, 0) would be located (-1, 0) after the reflection and (1 + 8, 0 - 3) or (9, - 3) after the horizontal and vertical shifts..
over the y-axis and then shift (move) the reflected graph to the right 8 units and down 3 units. The point (1, 0) would be located (-1, 0) after the reflection and (1 + 8, 0 - 3) or (9, - 3) after the horizontal and vertical shifts..
If you would like to review another example, click on Example.

[Exponential Rules]
[Logarithms]
[Algebra]
[Trigonometry ]
[Complex Variables]
 S.O.S MATHematics home page
S.O.S MATHematics home page

Copyright © 1999-2004 MathMedics, LLC. All rights reserved.
Math Medics, LLC. - P.O. Box 12395 - El Paso TX 79913 - USA
 GRAPHS OF LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS
GRAPHS OF LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS  GRAPHS OF LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS
GRAPHS OF LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS 
![]() and the function
and the function ![]() on the same rectangular coordinate system. and answer the following questions about each graph:
on the same rectangular coordinate system. and answer the following questions about each graph: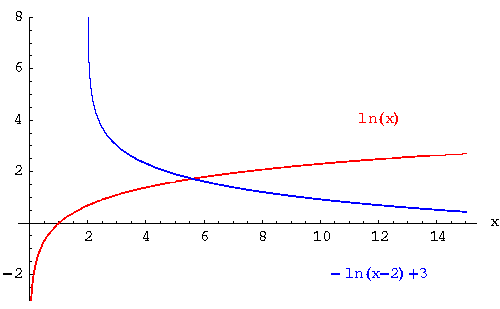
![]() and the function
and the function ![]() on the same rectangular coordinate system. Answer the following questions about each graph:
on the same rectangular coordinate system. Answer the following questions about each graph: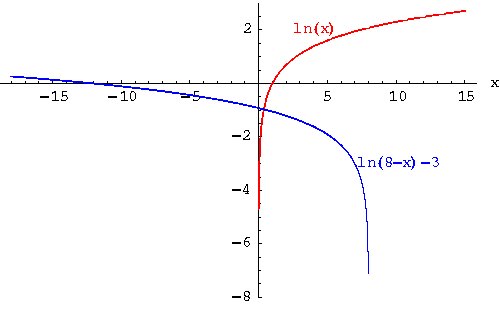
![]() crosses the x-axis at -12.085537 because
crosses the x-axis at -12.085537 because ![]() when x = -12.085537. It crosses the y-axis at -0.920558 because
when x = -12.085537. It crosses the y-axis at -0.920558 because ![]() .
.![]() over the y-axis and then shift (move) the reflected graph to the right 8 units and down 3 units. The point (1, 0) would be located (-1, 0) after the reflection and (1 + 8, 0 - 3) or (9, - 3) after the horizontal and vertical shifts..
over the y-axis and then shift (move) the reflected graph to the right 8 units and down 3 units. The point (1, 0) would be located (-1, 0) after the reflection and (1 + 8, 0 - 3) or (9, - 3) after the horizontal and vertical shifts..
 S.O.S MATHematics home page
S.O.S MATHematics home page 