 SOLVING EXPONENTIAL EQUATIONS
SOLVING EXPONENTIAL EQUATIONS

To solve an exponential equation, take the log of both sides, and
solve for the variable.

Example 1: Solve for x in the equation  .
.
Solution:
-
- Step 1: Take the natural log of both sides:

-
- Step 2: Simplify the left side of the above equation using Logarithmic Rule 3:

-
- Step 3: Simplify the left side of the above equation: Since Ln(e)=1, the equation reads

Ln(80) is the exact answer and x=4.38202663467 is an approximate answer because we have rounded the value of Ln(80)..
Check: Check your answer in the original equation.

Example 2: Solve for x in the equation 
Solution:
-
- Step 1: Isolate the exponential term before you take the common log of both sides. Therefore, add 8 to both sides:

-
- Step 2: Take the common log of both sides:

-
- Step 3: Simplify the left side of the above equation using Logarithmic Rule 3:
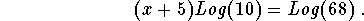
-
- Step 4: Simplify the left side of the above equation: Since Log(10) = 1, the above equation can be written

-
- Step 5: Subtract 5 from both sides of the above equation:

is the exact answer. x = -3.16749108729 is an approximate answer..
Check: Check your answer in the original equation. Does

Yes it does.
Example 3: Solve for x in the equation

Solution:
-
- Step 1: When you graph the left side of the equation, you will note that the graph crosses the x-axis in two places. This means the equation has two real solutions.
-
- Step 2: Rewrite the equation in quadratic form:

-
- Step 3: Factor the left side of the equation:

can now be written

-
- Step 4: Solve for x. Note: The product of two terms can only equal zero if one or both of the two terms is zero.
-
- Step 5: Set the first factor equal to zero and solve for x: If
 , then
, then  and
and  and
x=Ln(2) is the exact answer or
and
x=Ln(2) is the exact answer or 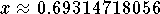 is an approximate answer.
is an approximate answer.
-
- Step 6: Set the second factor equal to zero and solve for x: If
 , then
, then  and
and  and x=Ln(3) is the exact answer or
and x=Ln(3) is the exact answer or  is an approximate answer. The exact answers are Ln(3) and Ln(2) and the
approximate answers are 0.69314718056 and 1.09861228867.
is an approximate answer. The exact answers are Ln(3) and Ln(2) and the
approximate answers are 0.69314718056 and 1.09861228867.
Check: These two numbers should be the same numbers where the graph crosses the x-axis.
Remark: Why did we choose the Ln in Example 3? Because we know that Ln(e) = 1.
If you would like to review another example, click on
Example.
Work the following problems. If you want to review the answer and the
solution, click on answer.
Problem 1: Solve for x in the equation 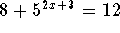 .
.
Answer
Problem 2: Solve for x in the equation  .
.
Answer
Problem 3: Solve for x in the equation  .
.
Answer
Problem 4: Solve for x in the equation  .
.
Answer
Problem 5: Solve for x in the equation 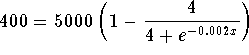 .
.
Answer
Problem 6: Solve for x in the equation 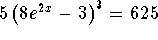 .
.
Answer

[Menu Back to Exponential Functions]
[Go on to Solving Logarithmic Equations]
[Algebra]
[Trigonometry]
[Complex
Variables]
 S.O.S MATHematics home page
S.O.S MATHematics home page

Copyright © 1999-2004 MathMedics, LLC. All rights reserved.
Math Medics, LLC. - P.O. Box 12395 - El Paso TX 79913 - USA
 SOLVING EXPONENTIAL EQUATIONS
SOLVING EXPONENTIAL EQUATIONS  SOLVING EXPONENTIAL EQUATIONS
SOLVING EXPONENTIAL EQUATIONS 

![]() .
.![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() .
. .
.![]() .
. .
.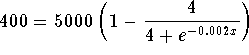 .
.![]() .
.
 S.O.S MATHematics home page
S.O.S MATHematics home page