 SOLVING LOGARITHMIC EQUATIONS
SOLVING LOGARITHMIC EQUATIONS SOLVING LOGARITHMIC EQUATIONS
SOLVING LOGARITHMIC EQUATIONS
Note:
If you would like an in-depth review of logarithms, the rules of logarithms, logarithmic functions and logarithmic equations, click on logarithmic function.
Solve for x in the following equation.
Example 1:
The above equation is valid only if
![]() or
or
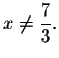 The domain is the set of real numbers not equal to
The domain is the set of real numbers not equal to
![]()
Convert the equation to an exponential equation with base 4.
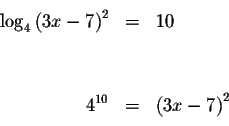
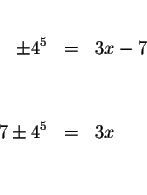
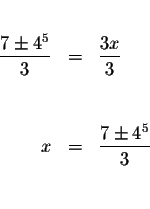
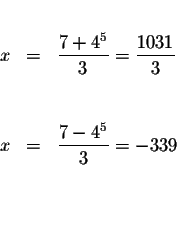
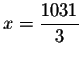 and
and
These answers may or may not be the solutions. You must check them with the
original equation, either by a numerical substitution or by graphing.
Numerical Check:
Check the answer
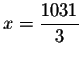 by substituting
by substituting
![]() in the original equation for x. If the left side of the equation equals the
right side of the equation after the substitution, you have found the
correct answer.
in the original equation for x. If the left side of the equation equals the
right side of the equation after the substitution, you have found the
correct answer.
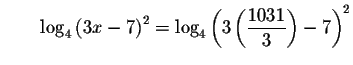
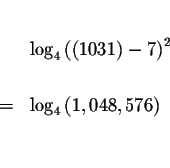
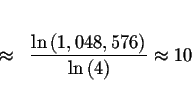
Since the left side of the original equation is equal to the right side of
the original equation after we substitute the value
![]() for x,
then
for x,
then
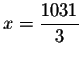 is a solution.
is a solution.
Check the answer x=-339 by substituting -339 in the original
equation for x. If the left side of the equation equals the right side of
the equation after the substitution, you have found the correct
answer.
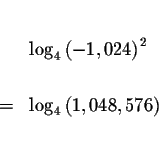
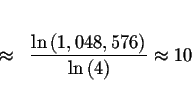
Since the left side of the original equation is equal to the right side of the original equation after we substitute the value -339 for x, then x=-339 is a solution.
Graphical Check:
You can also check your answer by graphing
![]() (formed by subtracting the right side of the
original equation from the left side). Look to see where the graph crosses
the x-axis; that will be the real solution. Note that the graph crosses the
x-axis at
343.6666666667 and -339. This means that
343.6666666667 and -339 are the real solutions.
(formed by subtracting the right side of the
original equation from the left side). Look to see where the graph crosses
the x-axis; that will be the real solution. Note that the graph crosses the
x-axis at
343.6666666667 and -339. This means that
343.6666666667 and -339 are the real solutions.
You may have to change the original equation somewhat to graph it because
most graphing calculators only have the natural log function and the common
log function. Rewrite the original equation
![]() in the equivalent form
in the equivalent form
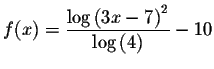 and graph it
and graph it
Recall that
![]() is equivalent to
is equivalent to
![]() only for those values of
only for those values of
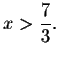 Why is
that? The domain of
Why is
that? The domain of
![]() is the set of real
numbers
is the set of real
numbers
![]() ,
and the domain of
,
and the domain of
![]() is the set of real numbers
is the set of real numbers
![]()
If you would like to work another example, click on example.
If you would like to test yourself by working some problems similar to this
example, click on problem.
If you would like to go to the next section, click on next.
If you would like to go back to the previous section, click on previous.
If you would like to go back to the equation table of contents, click on
contents.
This site was built to accommodate the needs of students. The topics and problems are what students ask for. We ask students to help in the editing so that future viewers will access a cleaner site. If you feel that some of the material in this section is ambiguous or needs more clarification, or you find a mistake, please let us know by e-mail.

