 SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS in TWO VARIABLES
SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS in TWO VARIABLES SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS in TWO VARIABLES
SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS in TWO VARIABLES
A system of equations is a collection of two or more equations with the same set of unknowns. In solving a system of equations, we try to find values for each of the unknowns that will satisfy every equation in the system.
The equations in the system can be linear or non-linear. This tutorial
reviews systems of linear equations.
A problem can be expressed in narrative form or the problem can be expressed
in algebraic form.
Let's start with an example stated in narrative form. We'll convert it to an
equivalent equation in algebraic form, and then we will solve it.
Problem 2.1d:
Five hundred tickets were sold for a certain music concert. The tickets for
the adults and children sold for $7.50 and $4.00, respectively, and the
total receipts for the performance were $3,312.50. How many of each kind of
ticket were sold?
Answer: 375 adult tickets were sold and 125 children tickets were
sold.
Solutions:
Essentially you have two sentences: one sentence deals with the total amount
of tickets and the other sentence deals with how much money was paid for the
tickets.
One sentence could be rewritten as ''the total amount adult tickets'' plus
''the total amount of children tickets'' equals 500 tickets. The second
sentence could be rewritten as ''the amount of adult tickets'' times $7.50
plus ''the amount of children tickets'' times $4.00 equals
$3,312.50
Let's rewrite the sentences again.
Sentence (1): ''the total amount adult tickets'' + ''the total amount of
children tickets'' = 500
Sentence (2):
![]() ''the total amount adult tickets'' +
''the total amount adult tickets'' +
![]() ''the total amount of children tickets'' = 3
''the total amount of children tickets'' = 3
It is going to become tiresome writing the phrases ''the total amount adult
tickets'' and ''the total amount of children tickets'' over and over.
Therefore, let the symbol x represent the phrase ''the total amount adult
tickets'', and let the symbol y represent the phrase ''the total amount of
children tickets''
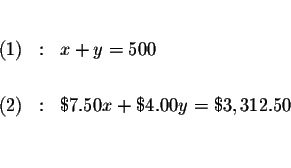
A system of linear equations can be solved four different ways:
Substitution
Elimination
Matrices
Graphing
The Method of Substitution:
The method of substitution involves several steps:
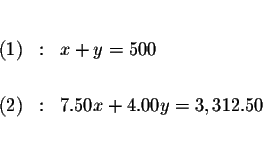
Solve for x in equation (1).
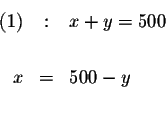
Step 2:
Substitute this value for x in equation (2). This will change equation (2)
to an equation with just one variable, y.
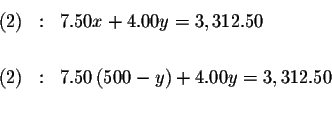
Step 3:
Solve for y in the translated equation (2).
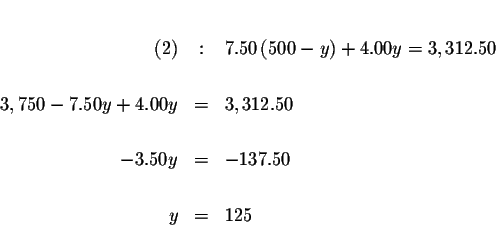
Step 4:
Substitute this value of y in equation (1) and solve for x.
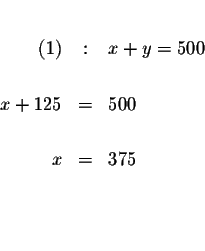
Step 5:
Check your answers by substituting the values of x and y in each of the
original equations. If, after the substitution, the left side of the
equation equals the right side of the equation, you know that your answers
are correct.
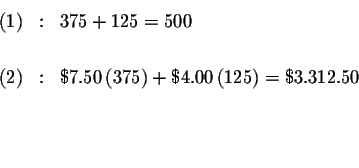
The process of substitution involves several steps:
In a two-variable problem rewrite the equations so that when the equations
are added, one of the variables is eliminated, and then solve for the
remaining variable.
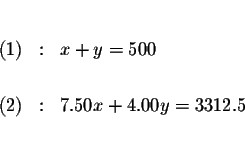
Multiply equation (1) by -4 and add it to equation (2) to form equation
(3) with just one variable.
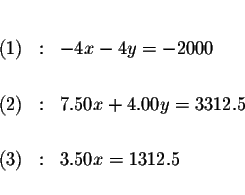
Solve for x.
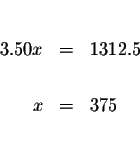
Substitute x=375 in equation (1) and solve for x.
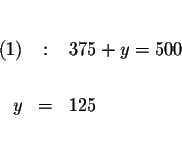
Check your answers.
The Method of Matrices:
This method is essentially a shortcut for the method of elimination.
Rewrite equations (1) and (2) without the variables and operators. The left
column contains the coefficients of the x's, the middle column contains
the coefficients of the y's, and the right column contains the
constants.
![$
\begin{array}{r}
(1) \\
\\
(2)
\end{array}
\left[
\begin{array}{rrrr...
...
& & & & \vert & & \\
7.50 & & 4 & & \vert & & 3312.5
\end{array}
\right] $](img16.gif)
The objective is to reorganize the original matrix into one that looks like
![$
\begin{array}{r}
(1) \\
\\
(2)
\end{array}
\left[
\begin{array}{rrrr...
...
& & & & \vert & & \\
0 & & 1 & & \vert & & b
\end{array}
\right] \bigskip $](img17.gif)
Step 1.
Manipulate the matrix so that the number in cell 11 (row 1-col 1) is 1. Cell
11 already has a 1.
Step 2:
Manipulate the matrix so that the number is cell 21 (row 2-col 1) is 0. Do
this by adding -7.50 times row 1 to row 2 to form a new row 2.
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
-7.50\left[ Row\ 1\right] +\left[ row\ 2\right] &=&\left[ New\ Row\ 2\right]
\\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img18.gif)
![$
\begin{array}{r}
(1) \\
\\
(2)
\end{array}
\left[
\begin{array}{rrrr...
...
& & & & \vert & & \\
0 & & -3.5 & & \vert & & -437.5
\end{array}
\right] $](img19.gif)
Manipulate the matrix so that the cell 22 is 1. Do this by multiplying row 2
by
![]() .
.
![$
\begin{array}{r}
(1) \\
\\
(2)
\end{array}
\left[
\begin{array}{rrrr...
...00 \\
& & & & \vert & & \\
0 & & 1 & & \vert & & 125
\end{array}
\right] $](img21.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
-1[Row\ 2]+[Row\ 1] &=&[New\ Row\ 1] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img22.gif)
![$
\begin{array}{r}
(1) \\
\\
(2)
\end{array}
\left[
\begin{array}{rrrr...
...75 \\
& & & & \vert & & \\
0 & & 1 & & \vert & & 125
\end{array}
\right] $](img23.gif)
The method of Graphing:
In this method solve for y in each equation and graph both. The point of
intersection is the solution.
If you would like to go back to the problem page, click on Problem.
If you would like to review the solution to the next problem, click on Problem
If you would like to return to the beginning of the two by two system of equations, click on Example.

