 GRAPHS OF LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS
GRAPHS OF LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS GRAPHS OF LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS
GRAPHS OF LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS
In this section we will illustrate, interpret, and discuss the graphs of logarithmic functions. We will also illustrate how you can use graphs to HELP you solve logarithmic problems.
(Reflection across the x-axis):
Whenever the minus sign (-) is in front of the function notation, it indicates a reflection across the x-axis. For example, the graph of - f(x) is a reflection of the graph of f(x) across the x-axis. The graph of 3 - g(x) involves the reflection of the graph of g(x) across the x-axis and the upward shift of the reflected graph 3 units.
Example 1:
Graph the function ![]() and the function
and the function ![]() on the same rectangular coordinate system. and answer the following questions about each graph:
on the same rectangular coordinate system. and answer the following questions about each graph:
In what quadrants is the graph of the function ![]() located?
located?
What is the x-intercept and the y-intercept on the graph of the function ![]() ?
?
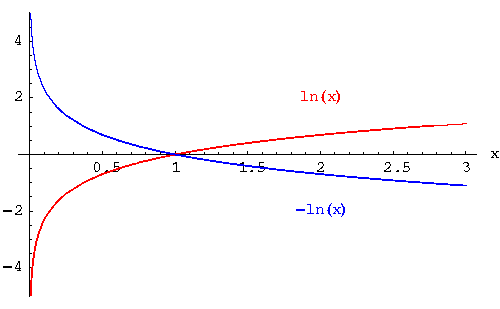
|
The graph to the right of the y-axis is the graph of the function ![]() , and the graph on the left to the left of the y-axis is the graph of the function
, and the graph on the left to the left of the y-axis is the graph of the function ![]() .
.
This means both graphs are symmetric to each other with respect to the x-axis. What exactly does that mean? Well for one thing, it means if there is a point (a, b) on the graph of ![]() , we know that the point (a, - b) is located on the graph of
, we know that the point (a, - b) is located on the graph of ![]() .
.
The shapes are the same. The graph of ![]() is a reflection over the x-axis of the graph of
is a reflection over the x-axis of the graph of ![]() .
.
If you would like to review examples on the following, click on Example:
Reflection over the y-axis: The graph of f(x) versus the graph of f(-x). Example.
Vertical shifts: The graph of f(x) versus the graph of f(x) + C. Example.
Horizontal shifts: The graph of f(x) versus the graph of f(x + C) Example.
Combination horizontal shift and reflection across the y-axis: The graph of f(x) versus the graph of f(- x + C) or f(C - x) Example.
Combination horizontal and vertical shifts: The graph of f(x) versus the graph of f(x + A) + B Example.
Combination horizontal and vertical shifts and reflections: The graph of f(x) versus the graphs of -f(x) + C. f(-x) + C, f(x + C) + D. Example.
Stretch and Shrink: The graph of f(x) versus the graph of C(x). Example.
Stretch and Shrink: The graph of f(x) versus the graph of f(Cx). Example.
Combination of stretch, shrink, reflection, horizontal, and vertical shifts: Example.
Solving an equation from a graph: Example.

 S.O.S MATHematics home page
S.O.S MATHematics home page 