 The Mean-Value Theorem
The Mean-Value Theorem
 The Mean-Value Theorem
The Mean-Value Theorem
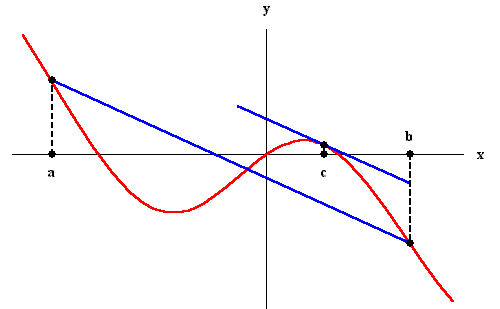
The Mean Value Theorem is one of the most important
theoretical tools in Calculus. It states that if f(x) is
defined and continuous on the interval [a,b] and differentiable
on (a,b), then there is at least one number c in the interval
(a,b) (that is a < c < b) such that
 |
Example. Let
 ,
a = -1and b=1. We have
,
a = -1and b=1. We have
Remark. It is clear that the derivative of a constant
function is 0. But you may wonder whether a function with
derivative zero is constant. The answer is yes. Indeed, let
f(x) be a differentiable function on an interval I, with
f '(x) =0, for every ![]() .
Then for any a and b in
I, the Mean Value Theorem implies
.
Then for any a and b in
I, the Mean Value Theorem implies
Exercise 1. Show that the equation
Exercise 2. Show that
has exactly one real root.
![]()
for all real numbers a and b. Try to find a more general
statement.
 S.O.S MATHematics home page
S.O.S MATHematics home page
Math Medics, LLC. - P.O. Box 12395 - El Paso TX 79913 - USA