 SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS in THREE VARIABLES
SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS in THREE VARIABLES SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS in THREE VARIABLES
SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS in THREE VARIABLES
It is often desirable or even necessary to use more than one variable to model a situation in many fields. When this is the case, we write and solve a system of equations in order to answer questions about the situation.
If a system of linear equations has at least one solution, it is
consistent. If the system has no solutions, it is inconsistent. If
the system has an infinity number of solutions, it is dependent.
Otherwise it is independent.
A linear equation in three variables describes a plane and is an equation
equivalent to the equation
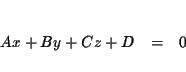
Problem 3.1a:
A total of $50,000 is invested in three funds paying 6%, 8%, and 10%
simple interest. The yearly interest is $3,700. Twice as much money is
invested at 6% as invested at 10%. How much was invested in each of the
funds.
Answer: $30,000 is invested at 6%, $5,000 is invested at 8%,
and $15,000 is invested at 10%
Solution:
There are three unknowns:

The first sentence can be rewritten as [ The amount of money invested at 6%
] + [ The amount of money invested at 8% ] + [ The amount of money
invested at 10% ]
![]() The second sentence can be rewritten 0.060 times [ The amount of money
invested at 6% ] + 0.08 times [ The amount of money invested at 8% ] + 0.10 times [ The amount of money invested at 10% ]
The second sentence can be rewritten 0.060 times [ The amount of money
invested at 6% ] + 0.08 times [ The amount of money invested at 8% ] + 0.10 times [ The amount of money invested at 10% ]
![]() The third sentence can be rewritten [ The amount of money invested at 6% ]
= twice [ The amount of money invested at 10% ].
The third sentence can be rewritten [ The amount of money invested at 6% ]
= twice [ The amount of money invested at 10% ].
It is going to get boring if we keep repeating the phrases


The first sentence can be rewritten as [ The amount of money invested at 6%
] + [ The amount of money invested at 8% ] + [ The amount of money
invested at 10% ]
![]() can now be written in the algebraic form
can now be written in the algebraic form
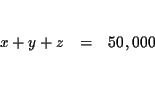
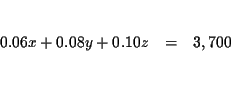
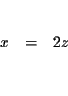
We have converted the problem from one described by words to one that is
described by three equations.
| x+y+z | = | 50,000 | (1) |
| 0.06x+0.08y+0.10z | = | 3,700 | (2) |
| x-2z | = | 0 | (3) |
1) Substitution,
2) Elimination
3) Matrices
SUBSTITUTION:
The process of substitution involves several steps:
Step 1: Solve for one of the variables in one of the equations. It
makes no difference which equation and which variable you choose. Let's
solve for x in equation (3).
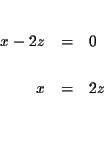
| x+y+z | = | 50,000 | |
| = | 50,000 | ||
| y+3z | = | 50,000 | (4) |
| 0.06x+0.08y+0.10z | = | 3,700 | |
| = | 3,700 | ||
| 0.08y+0.22z | = | 3,700 | |
| 8y+22z | = | 370,000 | |
| 4y+11z | = | 185,000 | (5) |
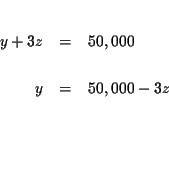
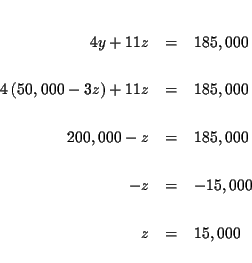
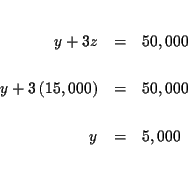
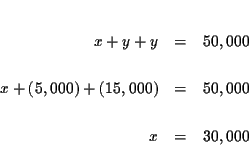

The process of elimination involves several steps: First you reduce three
equations to two equations with two variables, and then to one equation with
one variable.
Step 1: Decide which variable you will eliminate. It makes no
difference which one you choose. Let us eliminate y first because y is
already missing from equation (3).
| x+y+z | = | 50,000 | (1) |
| 0.06x+0.08y+0.10z | = | 3,700 | (2) |
| x-2z | = | 0 | (3) |
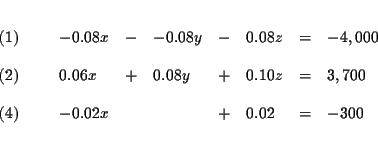
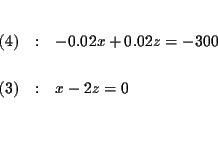
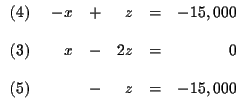
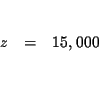
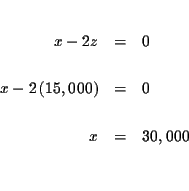
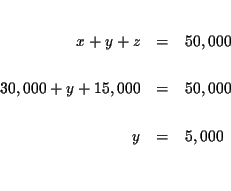
MATRICES:
The process of using matrices is essentially a shortcut of the process of
elimination. Each row of the matrix represents an equation and each column
represents coefficients of one of the variables.
Step 1:
Create a three-row by four-column matrix using coefficients and the constant
of each equation.
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
&&
\begin{array}{r}
(1) \\
\\
(2) \\
\\
(3)
...
...t & \\
x & & & & -2 & \vert & 0
\end{array}
\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img36.gif)
The vertical lines in the matrix stands for the equal signs between both
sides of each equation. The first column contains the coefficients of x, the
second column contains the coefficients of y, the third column contains the
coefficients of z, and the last column contains the constants.
We want to convert the original matrix
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
&&
\begin{array}{r}
(1) \\
\\
(2) \\
\\
(3)
...
...t & \\
1 & & & & -2 & \vert & 0
\end{array}
\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img36.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
&&
\begin{array}{r}
(1) \\
\\
(2) \\
\\
(3)
...
... & \\
0 & & 0 & & 1 & \vert & c
\end{array}
\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img38.gif)
Step 2: We work with column 1 first. The number 1 is already in cell
11(Row1-Col 1). Add -0.06 times Row 1 to Row 2 to form a new Row 2, and
add -1 times Row 1 to Row 3 to form a new Row 3.
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
-0.06\left[ Row\ 1\right] +\left[ Row\ 2\right] &=&\lef...
...ght] +\left[ Row\ 3\right] &=&\left[ New\ Row\ 3\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img39.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
&&
\begin{array}{r}
(1) \\
\\
(2) \\
\\
(3)
...
...0 & & -1 & & -3 & \vert & -50,000
\end{array}
\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img40.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
50\left[ Row\ 2\right] &=&\left[ New\ Row\ 2\right] \\
&& \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img41.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
&&
\begin{array}{r}
(1) \\
\\
(2) \\
\\
(3)
...
...0 & & -1 & & -3 & \vert & -50,000
\end{array}
\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img42.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
-1\left[ Row\ 2\right] +\left[ Row\ 1\right] &=&\left[ ...
...ght] +\left[ Row\ 3\right] &=&\left[ New\ Row\ 3\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img43.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
&&
\begin{array}{r}
(1) \\
\\
(2) \\
\\
(3)
...
...
0 & & 0 & & -1 & \vert & -15,000
\end{array}
\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img44.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
-1\left[ Row\ 3\right] &=&\left[ New\ Row\ 3\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img45.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
&&
\begin{array}{r}
(1) \\
\\
(2) \\
\\
(3)
...
...
0 & & 0 & & 1 & \vert & 15,000
\end{array}
\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img46.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
\left[ Row\ 3\right] +\left[ Row\ 1\right] &=&\left[ Ne...
...ght] +\left[ Row\ 2\right] &=&\left[ New\ Row\ 2\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img47.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
&&
\begin{array}{r}
(1) \\
\\
(2) \\
\\
(3)
...
...
0 & & 0 & & 1 & \vert & 15,000
\end{array}
\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img48.gif)
If you would like to go back to the problem page, click on Problem.
If you would like to review the solution to the next problem, click on Problem
If you would like to return to the beginning of the three by three system of equations, click on Example.

